On page SEO is the practice of designing, and putting together the structure of a web page, in a manner that meets a search engines quality requirements to rank highly (on-page), answers a searchers question (on and off-page), and promotes the website externally to other websites (off-page). On-page SEO extends beyond content to address things like meta descriptions and canonical tags, etc., albeit in brief.
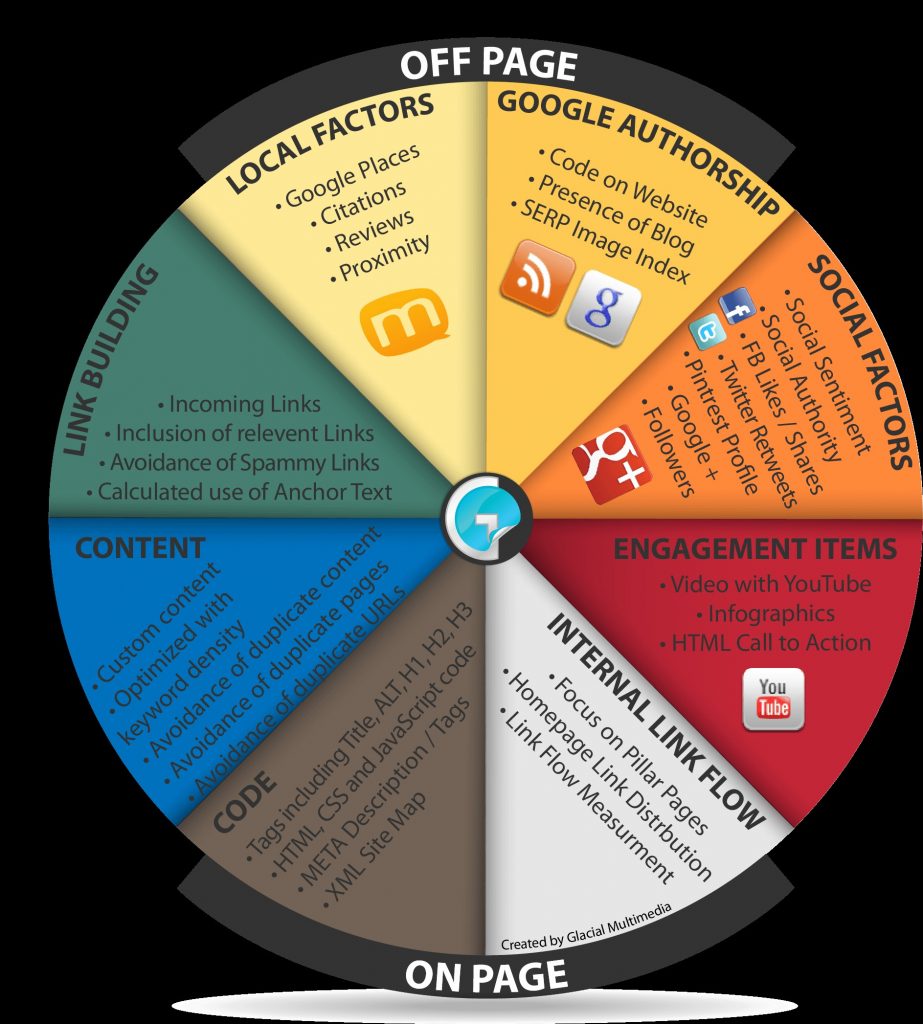
Image via Scarletts Web
While your site might get away without needing heavy implementation of off-page SEO, on-page SEO is essential to the performance of your website on a SERP. If on-page SEO is not properly integrated into your site, you can drastically reduce your chances of getting organic traffic to your site.
Let’s start with the basics – content creation.
Create Good Quality Content
Applying keyword research
When creating content, have this rule in mind, “Brilliant content will do well, with or without SEO. Bad content will not do well, with or without SEO.”
What is good content?
- Original content (text, articles, videos, images, infographics, presentations, comments, etc.)
- Exclusive content. Your original material published on another website must have canonical tags
- Text content. Include written text to accompany your non-text content.
- Publish useful content. Create content that adds value to your website and which is helpful to your viewers/readers
- Well researched content. Search engines are intelligent and prefer well-crafted content. Your site’s users also want to read coherent and well-prepared content
In the articles preceding this one, we learnt how your target audience searches for content. Now, let us put that research into practice.
Here’s a simple outline to follow when applying keyword research.
Survey your keywords:
Group them according to intent and similar topics
The groups will be your pages. This method is preferable to creating individual pages for each keyword variation
Create a list of keywords – single, LSI, and longtail keywords. Use them in your headings, titles, descriptions, and content
Evaluate the SERP for every keyword or group of keywords:
- From the information gathered, determine the type and format of your content
- Look out for the following ranking page characteristics:
- Are they video or image-heavy?
- Is the content short and concise or long-form?
- Content formatting: Paragraphs, bullets, or lists?
- Ask, “What unique and valuable content can I offer to make my page enticing and better than the pages ranking for my keyword?”
On-page SEO enables you to convert your research into compelling and attractive content that your audience will love. Be careful not to use low-value tactics that’ll hurt you, more than help!
Avoiding Low-value Tactics
Your website should basically:
- Answer your sites users questions
- Guide the visitors through your site seamlessly – without any frustration
- Help anyone understand the intention and purpose of your site
Therefore, content is not supposed to be created for the purpose of ranking highly only. A site’s content should comprehensively meet the searcher’s need for answers, while ranking will help that searcher “find” your website more easily.
Focusing too much on ranking is putting the cart before the horse, therefore exposing your site to low-level content tactics, which will only serve to undermine the quality of your website.
Examples of low-level tactics are:
Thin content
An older content strategy used to be creating a page for every single iteration of keywords so as to rank on the SERP’s first page for those highly specific queries.
For instance, a bridal gown shop would create individual pages for “bridal dresses,” “wedding gowns,” and “bridal gowns,” even though each page was repetitive in its content. This strategy was effective because, at the time, Google couldn’t distinguish the relationship between a site’s pages.
However, thin content spread like wildfire through the web, and finally, Google had to address it with its 2011 update referred to as “Panda.” Panda penalizes low-quality web pages and rewards high-quality pages by giving them top spots on SERP’s.
In 2012, Google introduced Penguin, which is a tracking software that penalizes over-optimized anchor links, low-quality links, and link farms.
To this day, Google penalizes thin content and low-quality links with manual actions while also promoting good quality pages on its SERP. Getting a manual action or penalty from Google will ensure that a web page from your site or even your entire website, won’t appear in search results.
Google advises that a website should have a comprehensive page on a specific topic rather than multiple pages for each group of keywords or variations of a keyword.
Duplicate content
This is as it sounds; it refers to the content shared between domains or between several pages of a single domain. On the other hand, “scrapped content” goes a step further and uses material from other sites blatantly, without any authorization.
Scrapped content is either:
- Using content and republishing in its exact form or
- Modifying slightly, without adding any original information or value to it
There are, however, legitimate reasons for duplicate content, so Google permits the use of a rel=canonical tag to show the original version. Google doesn’t penalize duplicate content; it simply prioritizes those with a canonical (source) URL when displaying results on its search results page, to improve user experience.
Cloaking
According to search engine guidelines, the HTML code of your website should not contain text that a visitor to your website cannot view in the displayed content. The content that a visitor views should be the same as the one read by a search engine’s crawlers. When this tenet is not followed, search engines call it cloaking or “black hat cloaking,” which is penalized when discovered.
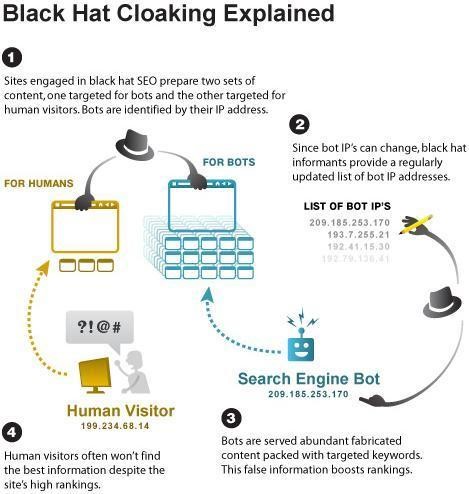
Cloaking is done for a number of reasons, in a variety of ways. Cloaking can be done for positive or negative reasons. Sometimes a website might “cloak” what is presented to a search engine in order to improve user experience. To be safe, follow Google guidelines on cloaking.
Keyword Stuffing
People are normally advised to use keywords that rank highly, repetitively, so as to be able to rank higher. They do not know that Google considers it “keyword stuffing” and penalizes it.

For example, you discover from keyword research that the top-ranking blog post on “Spring Bridal Gowns 2020” has the following number of single word or group keyword references as follows:
- Spring bridal gowns – 100 references
- Bridal gowns – 150 references
- Spring – 100 references, etc
Upon making that discovery, you decide to double or triple the word references to increase your chances of ranking highly. This is considered keyword stuffing. Another method of keyword stuffing is bolding all your targeted keywords.

Auto-generated content
This is arguably the most aggressive form of low-quality content. It is created programmatically and is auto-generated, with the intention of manipulating search rankings. Auto-generated content is spammy and contains incoherent messages. Auto-generated content is usually sent to the spam box folder of your email account.
Avoid low-value tactics and instead, focus on creating “10X content,” i.e., content that is 10X better than the highest-ranking web page in your category!
Optimize Meta Descriptions and Page Titles
Meta descriptions and page titles are vital for on-page SEO. Search engines specifically check for the page title and description of a page. They read them so that they can understand the purpose of the page and then rank your web page (for keywords) based on domain authority, competition, off-page SEO, among other considerations.
Page Titles
Each page should have a unique title on the browser tab window, that will help both the users and search engines understand what the web page is about.
A page with the title “On-page SEO checklist..” or “Neapolitan noise..” is preferable as compared to a page with “index.html.
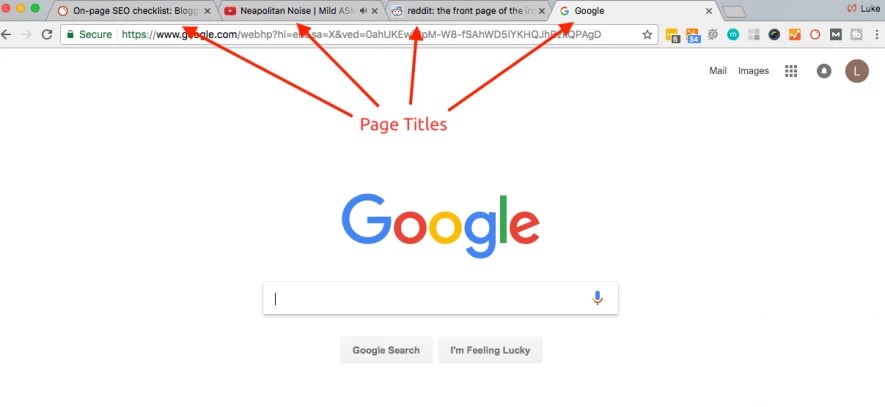
A page title is one of the most critical on-page SEO factors.
To optimize a page title:
- Add
keywords to the first set of page titles. This helps search
engines know, from the get-go, what keywords the page is targeting. Don’t force
it though, and avoid keyword stuffing
- Short descriptive titles. A title does not need to be long, 60 characters or less will suffice. In any case, Google shows less than 60 characters of the SERP title
- Include power words and numbers. Including power words, e.g., Actionable, ultimate, checklist, amazing, etc.,” with numbers, e.g., “10 Actionable..,” draws readers and increases their CTR
- Do not include the domain. Google automatically adds the domain name, so don’t add it to your title. However, if you have a powerful and recognizable brand, consider including your domain into your title
Meta Descriptions
A meta description box will describe on the SERP, in up to 200 characters, the content of your page. If a compelling read, it can draw users to your page. If not, most user will move on to the next web page.
Avoid auto-generated descriptions because they sometimes do not make sense. As good practice, also add your target keywords. Google highlights search terms, so the searcher will be drawn to any meta description that contains relevant keywords.
Optimize Page Content
In addition to keyword research using tools, for example, Moz Explorer, use these features by Google: People also ask for, Google suggest and Related searches.
- Google suggest
When typing a query on Google search, several options are provided for you to choose from. These are good keywords to use in your content
- People also ask
This is similar to Google suggests, where “people also ask” will present query results that you can use in your sub-headings
Image via MediaDigi
- Related searches
Google shows all your associated searches at the bottom of the SERP. Mention some of the words, without keyword stuffing
Headings and Content Formatting
A page should be formatted appropriately, with both a heading (h1) and subheadings (h2, h3).
You can have either the same <title> and <h1> tag, or get an alternative title for the heading. Search engines display the results of the title tag and not the h1 tag.
You should:
- Write useful and captivating headings. Avoid using single word headings
- Headings should be hierarchical i.e. tag 1 <h1>, tag 2 <h2>, tag 3 <h3>, etc.
- Use suggested keywords in your headings and subheadings and content
With content formatting:
- Ensure that the content is easy to read and comprehend
- Use italics, underline, or bold to highlight the essential parts of the content
- Use a large font, at least 15px
- Use small paragraphs containing 3-4 lines max
- Provide adequate spacing between paragraphs
- Use of CSS to make sections that stand out
Multimedia Elements
Images are essential for presentation purposes. They brighten up a page and make it more attractive, engaging, and easy to comprehend.
However, they slow down the speed of a page and can sometimes be challenging to understand if not correctly used.
SEO best practices for images are:
- Reference the source of images or use original images
- Reduce the size of the images – the lesser the bytes, the better
- Use an ALT tag for description purposes to help search engines understand the intention of the image
- Use descriptive file names, e.g., “man exercising.jpg” instead of “image 1.jpg.”
- Load your pages faster with a CDN – Content Delivery Network, if you have numerous images on a single page. A CDN will enable your images to be hosted by several servers, therefore speeding up the loading process
URL Optimization
To get the absolute best from SEO, optimize your URL. This features two parts: URL optimization and URL structure
Image via Neil Patel
URL Optimization.
A permanent link or slug is the URL of each page. Good URLs are less than 255 characters and also use hyphens “-“ to separate the different sections, e.g., “..puppies-adorably-confused-by-rainbow.”
Good SEO friendly URLs are: descriptive, short, and include target keywords.
Examples of bad URLs:
- https://www.digimarketing.com/p!162 or
- https://www.digimarketing.com/seotipsforbeginners/ or
- https://www.digimarketing.com/123131/publish/data2/seo_Tips.html
URL Structure.
A URL structure should look like the structure of a website.
URL best practices are:
- Use categories. Group your pages to help search engines and users find your pages faster. Don’t overuse subcategories.
For example:
Homepage > Social Media > Instagram > Article
Not…
Homepage > Social Media > Instagram > How To > Article
- Add a breadcrumb menu. It helps users navigate your website easily while keeping track of the home page.
Internal Links
Link pages within your website for optimization because:
- It’s like building your own web.
A search engine spider will first crawl through a site, looking for and following all links. If it doesn’t have any links within the page, it’ll read the content of your pages and then leave. If you have other links leading to the rest of your website, you’ll enable the spider to gather more info on your site, which will improve it’s ranking
- It informs a search engine about the most important pages.
Every site has anchor pages that are more important than the other pages. Internal links pinpoint the most important pages.
- It increases the time spent on your website.
A user interested in a particular topic will follow the links provided on your site and will spend time on it, therefore increasing the time spent on your website, and on the pages visited, and as a result, decrease the bounce rate.
Best practices are:
- Use keywords for both internal and external links
- Incorporate internal links only when they are useful to site users
- Add links to the main body of your page and not in the footer or sidebar
External Links
Google uses external links to understand the relevance of a site and its connection to specific topics. Linking to high-quality websites that are relevant increases the trustworthiness of your content, leading to improved SEO.
Webmasters are fearful of external links due to the misinformation surrounding the release of Panda and Penguin. Google doesn’t penalize the use of useful quality links to your site.
Page Loading Speed
Page speed is now an officially ranking speed due to Google’s quest to make the web faster. They plan to include the fastest websites to their index. Ensure that your page loads very quickly for SEO purposes and also for customer retention.
Mobile Friendliness
60% of searches are derived from mobile phones. Make sure that your site is mobile-friendly, and that the content is displayed correctly, including the CTA buttons. Check and fix potential problems with the Google mobile-friendly tool.
Comments and On-Page SEO
Comments are relevant today because they interact with your page and indicate what they like and what they don’t appreciate. Those who read or post comments spend time on your site, and that boosts your SEO.
Best practices
- Moderate all comments
- Only publish comments that are relevant to page content
- Don’t approve comments from fake names
- Respond to comments on your site
Now on to off-page SEO. If anyone asks, on-page SEO is more important, especially for new websites, because it builds the foundation for a good website and a solid SEO.
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO refers to the activities that you perform externally, outside your website. These activities are:
- Social media marketing
- Link building
- Brand mentions
Let’s start by examining the benefits of off-page SEO.
The Importance of Off-Page SEO
Off-page provides Google with a good picture of the relevance of your website to the outside world. A high-quality website will receive backlinks (references) from other websites. It is also more likely to enjoy mentions on social media; for example, Facebook shares, Tweets, Pins, etc.
A successful offsite strategy will benefit the owner in the following ways:
- Increase in rankings on SERPs, leading to more traffic
- Increase in PageRank. 0-10 is the number given to a website by Google, to indicate its importance
- Greater exposure leading to more visits, more links, and more social media mentions
- Establish trustworthiness through Google’s Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness (E-A-T). EAT establishes the expertise of a website on a subject matter via algorithms that indicate that relevant sites agree that your website provides expert information
Link Building
Building links to your website helps you get “voters” and is the most popular off-page SEO strategy. Basically, with many voters, you by-pass competitors and rank higher.
For example, a website referencing your site on their page tells search engines that you provide relevant information. Over the past couple of years, websites used to increase link counts through:
- Blog directories – Similar to yellow pages, with each entry pointing to a website
- Forum signatures – People participated in online forums with the sole purpose of obtaining a link back to their site. They provided their links in their forum signatures
- Comment link – Similar to forum signatures, except that one would comment on a number of websites or blogs with the purpose of getting a link back. Users wouldn’t use their names but would instead indicate, e.g., “ SEO guru comments.”
- Article Directories – Some directories accepted and published unique content, while others received material from any source. These published articles enabled websites to get a link, or more, to their websites
- Shared content directories – Sites published content where one could include links pointing to websites
- Link exchange schemes – Instead of posting content on the platforms mentioned above, websites cooperated with relevant sites and directly linked content from their sites to the other sites
All the methods listed above are now outdated and lead to penalties if attempted today.
Google approves of any links that are natural, where a website owner links to a different site simply because they like another blog or website. A good link has to have relevant anchor text.
Social Media Marketing
Off-site SEO comprises of social media marketing – it’s a form of link building. It would be good to note at this point that just about all social media links are “no-follow.” They are, however, still valuable. Proper configuration of SM profiles can also boost SEO.
Brand Mentions
Google loves brands. If you look at your SERPs, you’ll notice that most branded websites are ranked at the very top. This is because of the aforementioned E.A.T. Large brands are trusted by users, are more reliable, and this translates to happy Google users and better user experience.
Brand mentions do not usually have a link pointing to your website. Your site can be mentioned in articles, forums, social media networks, or reviews. Crawlers pick up these signals and evaluate them to get a picture of your brand as other sites perceive it. Your off-page SEO should strive to always pursue positive mentions of your products, services, or authors. Make sure to respond to any misleading or negative comments about your website.
