TECHNICAL SEO
Knowledge in the technical aspects of SEO will help you optimize your website for search engines as well as establish credibility with developers.
Technical SEO is the precise steps needed to optimize your site for both crawling and indexing. It is referred to as technical because it does not have anything to do with website content or site promotion.
Now that you understand what SEO is, it is essential to obtain a foundation on keyword research and how search engines work, so as to grasp the technical concepts contained in this article.

Index via Search Engine Journal
How Search Engines Work
To find a site on the vast world-wide-web, you probably type the address into your browser’s address bar. What happens when you don’t know the URL? Well, you would need to search for that particular site and other information using a search engine.
Finding Things Online
First off, think about the combination of words to use in your search – too many, and you’ll get an error; too few, and you’ll get irrelevant and misleading results.
For example, “What nations did the Vikings raid and conquer?” is unnecessarily wordy. Instead, save time and focus on specific keywords. Omit joining words and punctuation and search for the following keywords “nation Vikings raid conquer.”
Search Engines and Indexing
To locate what seek, a search engine will typically “crawl” its index of web pages for related content. The robotic program that accomplishes this is called a “spider” or “web crawler.” These spiders search for new and updated content. Content types vary and can be – an image, web page, PDF, video, etc. Regardless of the format, content is discovered and identified by links. Each time a web crawler visits a site, it creates a copy and adds the site’s URL to an index.
After that, the web crawler visits all the other links on that web page. It copies, indexes, and follows each link. The crawler repeats this process, building an extensive index of web pages as it goes along. Sometimes some websites use programs that hinder web crawlers from visiting their sites. These pages are not added to the index, together with any pages that people do not link to.
The gathered information then becomes the search engines index. A web crawler has visited every page that shows up on an SERP.
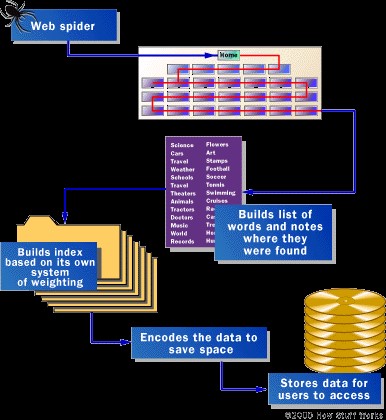
Image via How Stuff Works
How do Search Engines Organize Results?
Search engines organize results and present, or rank, those that they deem useful – from top-ranked to least ranked. PageRank is the best-known Google algorithm used to improve search results. In other words, think of PageRank as you would a popularity contest. A web page is considered useful and wins the PageRank popularity contest if numerous links point to it. It will appear higher up in the SERP compared to other web pages.
The web pages listed on the first page of the search engines result page are the ones that PageRank thinks are the best. Search engines are also very attentive to “signals” when calculating the order of web pages on SERPs. An example of a signal is, how often a site is updated, and if the domain is trustworthy.
Every search engine has a unique algorithm. This means that some websites will rank their results in a totally different order or may show results that are poles apart.
In summary, search engines have three main functions:
- Crawl: They scour the world-wide-web looking for content and examining the code or content for each URL that they encounter
- Index: They store and organize all content discovered during the crawling process. Once a page is indexed, it is entered into a popularity contest, in order to be displayed as a top result to relevant queries
- Rank: They provide the portions of content that best resolve a searchers query. Meaning that search engine results pages are organized starting with the most relevant to the least relevant result
For detailed information, read How Search Engines Work.
Keyword Research
Now that you have read on the functions of a search engine, and how web sites show up in search results, let’s understand what your audience is looking for.
What is keyword research? Keyword research is the SEO process of finding and analyzing popular search terms that people use in search engines.
Why is Keyword Research Important?
The power and objective of keyword research lies in determining the strategic words to use in the content of your website and how to craft and organize that content to satisfy both search engines and users. Keyword research is comparable to market research – understand your target market and how they search for products, services, or content.
Keyword research provides data that answers queries like:
- What are search engine users looking for?
- How many users are searching for a particular item?
- In what format do they want to receive that information?
Once you discover how your target audience searches for the content you provide, you will uncover an entirely new world of strategic SEO!
Ask Questions Before Researching
The very first step before conducting keyword research is – ask questions. It defeats the purpose of keyword research and SEO, if you do not understand:
- Your business’s (client’s company’s) objective’s
- Your customers
- Your customers’ goals
Finding the answers to the above questions will help you understand what your audience wants and what you want to rank for – two very different things. Successful SEO campaigns require that you focus on your audience’s proclivities and then use keyword data to hone in and package those insights into excellent content.
For example, J&L (a Seattle-based, organic dairy, sweets and pastry shop) has heard about SEO and needs your help to improve how often they show up in organic search results (pun intended). To help them, you may ask questions such as:
- What are your best-selling desserts, pastries, snacks, candy, ice-cream, chocolate, etc.?
- What types of desserts, pastries, snacks, candy, ice-cream, chocolate, etc. are people searching for?
- When are people searching for desserts, pastries, snacks, ice-cream, etc.? Does your data reveal any increased conversions during weekends, holidays, temperature spikes? Are there seasonal trends throughout the year, etc.
- How are your customers searching for ice cream?
- What questions do they ask?
- What terms and words do they use?
- Are the majority of searches from mobile devices or computers?
- Where are your clients located? Are they local, national, or international?
- More importantly, how can J&L help provide the best content about their sweets and pastries, to cultivate an on and offline community and fulfill what your clients are searching for?
Asking these questions will guide your planning and keyword research and enable you to craft better content.
What Terms are People Searching?
As individuals, we have unique ways of describing things, situations, what we do, etc. Think of keyword research in the same manner. How does your audience search for the service, product, or information you provide?
Answering this question is the most crucial step in keyword research.
Discovering keywords
You may have a few keywords that you want to rank for. These will be, for example, topics that your website talks about, services, or products – they are good keywords for your research, so start there!
Run your keywords through a keyword research tool to find out similar keywords and their monthly search volume. Using a keyword research tool will help you discover common questions, other keywords, and topics for your content that you might have missed. Determine which word variations are the most popular keywords.
Example
Let’s use the example of a company that specializes in designing wedding invitation cards. Your word search combination is “wedding invitation designs.” You may instead find highly searched and relevant terms like:’
- Wedding invitation designs free
- or Wedding invitation card design
- Wedding invitations
- also Wedding invitation
- Shutterfly wedding invitations
From the image below, you’ll be surprised to discover that the keyword “wedding invitations” has a whooping monthly search volume of 118k-300k!
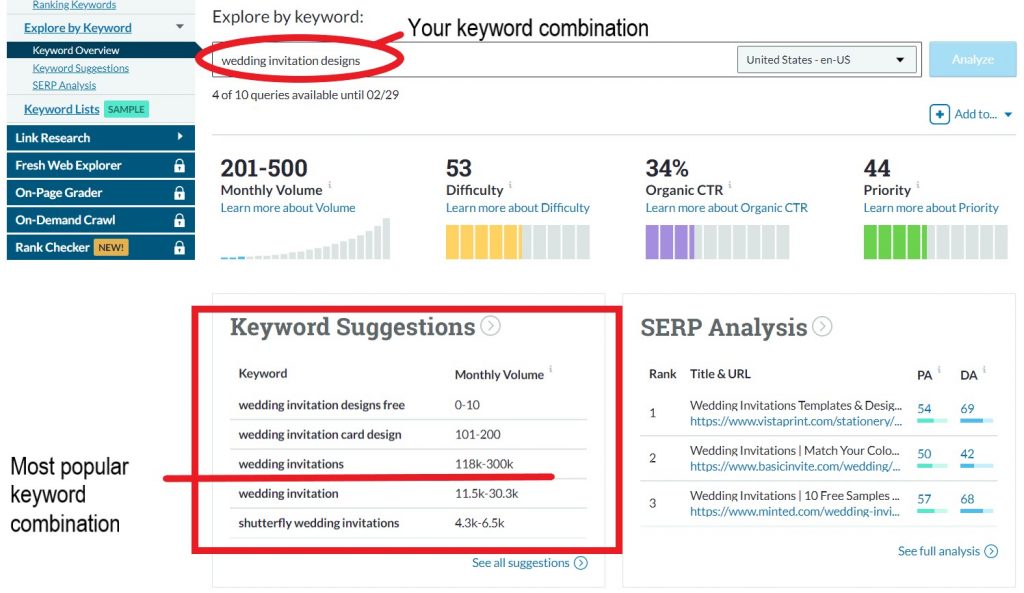
While looking for keywords that are relevant to your content, you will notice that the search volume varies greatly. In as much as you want to use the exact terms that your audience is searching for, sometimes it’s better to use search terms with lower search volume – they are less competitive.
Therefore, make it a practice to incorporate both high and low-competition keywords into your content to give your web page the most significant strategic advantage.
It is important to note that web pages rank for keywords and not entire websites. With big brand websites, you will often find that the homepage is ranking highly for several keywords. However, this isn’t usually the norm. Most websites receive more organic traffic to their web pages and not their homepages. Leading to the main reason why you should diversify your web pages by optimizing each page for unique and valuable keywords.
Frequency of Searches
“Keyword difficulty” is the term used to describe when it is difficult to achieve higher ranking due to a high search volume for a specific keyword or keyword phrase. Keyword difficulty is sometimes caused by big brands using lots of SERP features that clog up the results page, e.g., knowledge graph, carousels, featured snippets, etc. Big brands can take up the top ten results for high-volume keywords, so the battle for ranking can take years of effort to win.
So, the higher the search volume number, the tougher it is to achieve top organic ranking. Aim for a median search volume number – too high, and it’ll take too long for your site to get noticed. Too low, and you will miss out on drawing searchers to your site.
Read more on keyword research on HubSpot and Moz.
Technical SEO Optimization
Now that you have a solid foundation on SEO basics, it is essential to develop your developer’s language and grasp certain technical aspects of a websites formation and SEO.
Because the technical structure of a site will have a considerable impact on its performance, everyone needs to understand the following principles. In the section above, we spoke on how search engines work, and we also mentioned the crawling, indexing, and ranking process.
There are three main pillars of SEO: On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Technical SEO.
On-Page SEO: Is about content and how to make it relevant to the user’s search processes
Off-Page SEO: Also known as link building, refers to the process of acquiring mentions or links from other sites to increase trust during ranking
Technical SEO: Refers to the crawling and indexing process
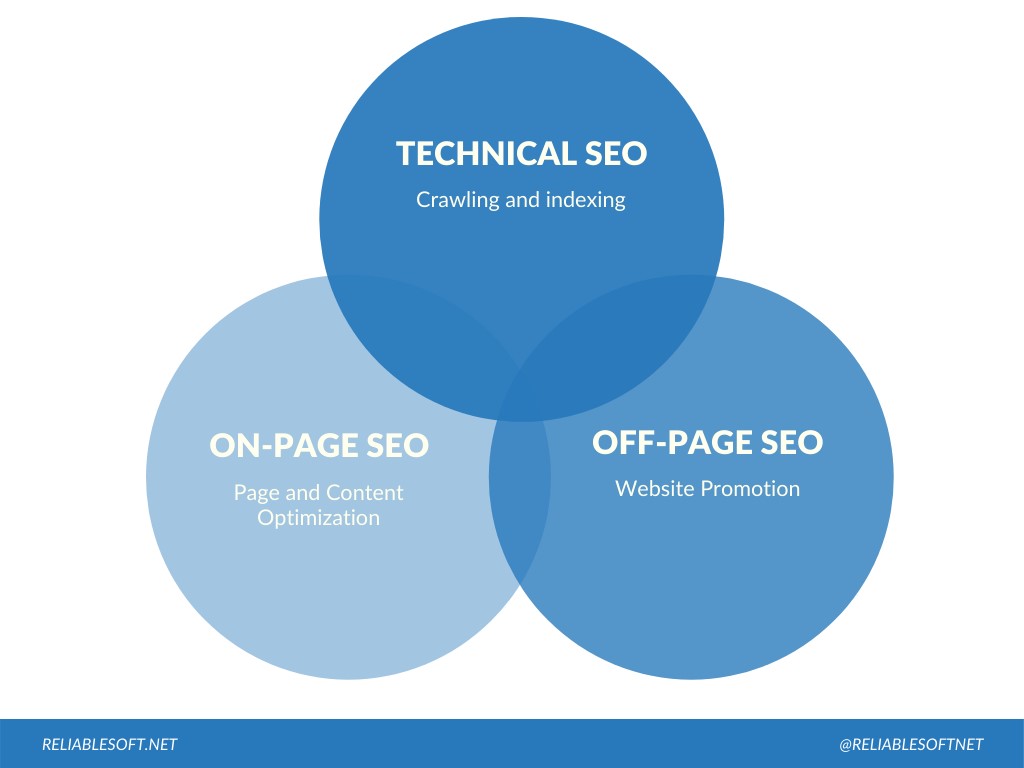
Image via Reliable Soft
It is evident from the above image that technical SEO, off-page SEO, and on-page SEO have to work in tandem to produce a fully optimized website.
Technical SEO Best Practices
A website’s creation begins from domain purchase, up to the point when it is fully rendered in a browser. The rendering path is an especially critical component of a site’s journey because that is when a browser turns a website’s code into a page that a noncoder, i.e., a non-techie, can read and comprehend.
Therefore, it is important to have technical SEO best practices because:
- The page assembly process can affect page speed or load times. Good speed is essential for keeping users on your website. It is also a ranking factor on Google and other search engines
- Google renders, e.g., JavaScript, the second time around (second pass). It will examine a page without scanning JavaScript, and then a while later, it will render JavaScript. This means that SEO-critical elements using JavaScript might not get indexed.
Think of a website loading in the same manner that you would think of your commute. When driving, say, you come across a gridlock, and you’re forced to sit in your car until it clears up. Sometimes you may leave an essential document on the table and have to return to get it. You may also run out of the house, briefcase in hand, wearing mismatched socks. This example paints a picture of an inefficient website.
This section will teach you how to implement technical SEO best practices to diagnose website inefficiencies and help you streamline them to improve user experience and gain positive rankings.
Lets begin.
Specify a Domain
When setting up your blog or website, you need to buy a preferred domain. Therefore:
- Purchase a domain name, e.g., jandlsweets.com. These are purchased from domain name registers such as HostGator or GoDaddy. These organizations are but two of several registries that manage domain name reservations
- Ensure that the domain name is linked to the IP address. The Internet does not comprehend names like “jandlsweets.com” without domain name servers (DNS). The Internet uses Internet protocol (IP) addresses, which are sets of numbers. For example, 124.0.0.1. Human beings will not go out of their way to remember the names of websites in number form, hence, jandlsweets.com. DNS links machine-readable names with human-readable names.
Make sure that the website is accessible with or without “www” in front of a domain name
For example, if your domain is “jandlsweets.com,” your website can be accessed through both “http://www.jandlsweets.com” and http://jandlsweets.com – without the “www.”
If you do not include both variations, you will encounter indexing issues, loss of page ranking, and duplicate content because searching engines will consider them to be two different websites.
Using “www” or not using it is a matter of personal preference and does not affect SEO in any way. Some people prefer using a plain “http://” and others “http://www.” What is important is informing search engines about your preferred website address name and being constant in using that preferred domain. One typically uses canonical URLs to do so – read on to find out about canonical URLs.
If you change your mind about the URL, you can always switch between the different formats with 301 redirections. However, this is not recommended because there are always risks when making domain migrations.
Optimize your Robots.txt
Upon setting your preferred domain, you can now optimize your robots.txt file.
Robots.txt is a text file that resides in the root directory of your site, which gives instructions to search engines on which web pages to crawl and index. The file format is simple, and in most cases, you do not need to make any changes to it.
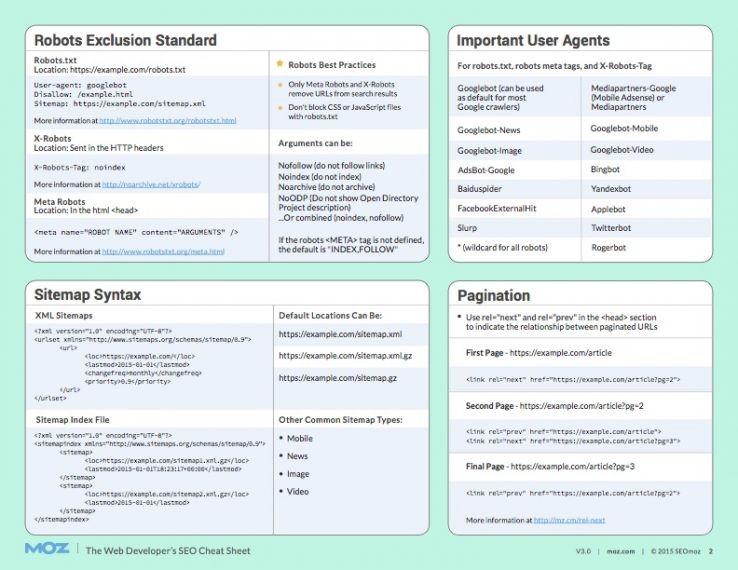
Image via Moz

Image via Backlinko
Optimize your URL Structure
Periodically check-up on your site’s URL structure/format.
URL best SEO practices state:
- Use lowercase letters
- Use – to separate URL words
- Make URL words short and descriptive
- Avoid unnecessary words or characters
- Use target keywords, do not keyword stuff
Only optimize your site’s URLs when putting up and publishing new content. It’s not recommended that you change your permanent link structure because there’s scarcely any benefit in doing so, but if you do, to be safe, use 301 redirects.
If using WordPress as your CMS, this process is automatic. WordPress creates your URL from your post title. Meaning that if you have a long title, you get a long URL.
For example, if your title is, “10 Beautiful Shades of Color for your Summer Events,” the URL generated will be http://jandlsweets.com/10-beautiful-shades-of-color-for-your-summer-events.
You could always shorten it to: http://jandlsweets.com/10-beautiful-shades-events, which is much simpler to remember.
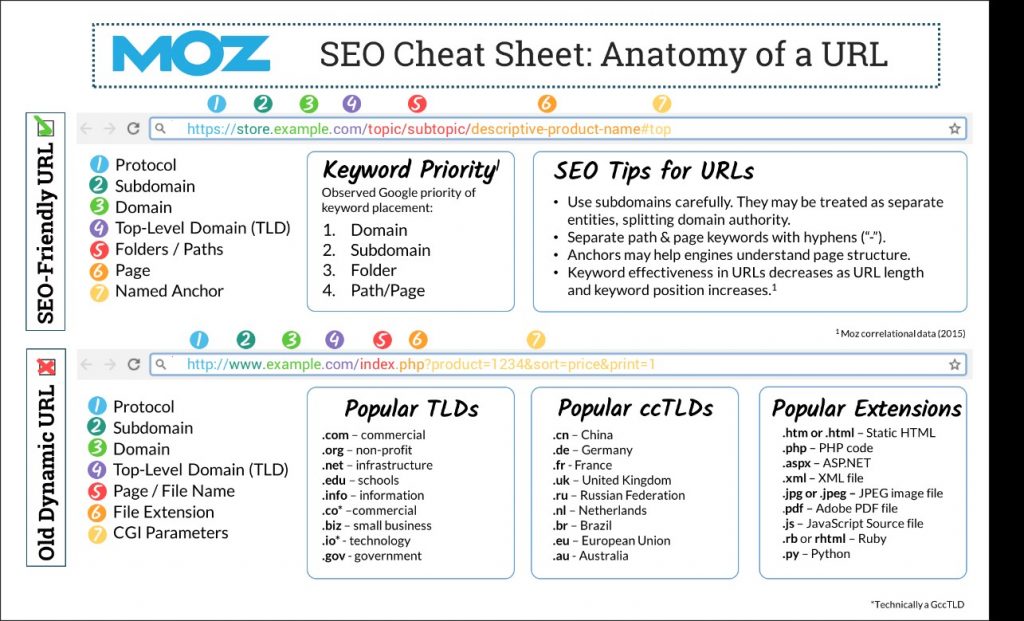
Image via Moz
Navigation and Website Structure
Website structure is vital to SEO because users will stay on longer and find what they want faster, while search engines can index a website easier with proper site structure.
Google considers a website’s structure, so, for example, don’t hide your archive pages or put content on a single page – that is wrong SEO practice!
Google has provided the following guidelines for website structure.
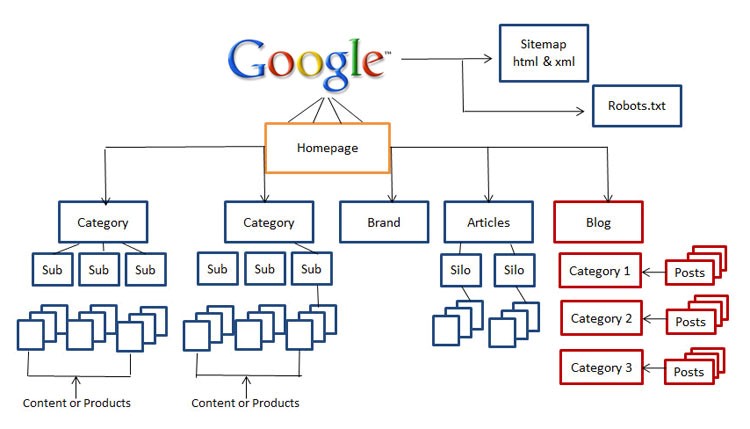
Image via Diffy Web
Add Breadcrumb Menus
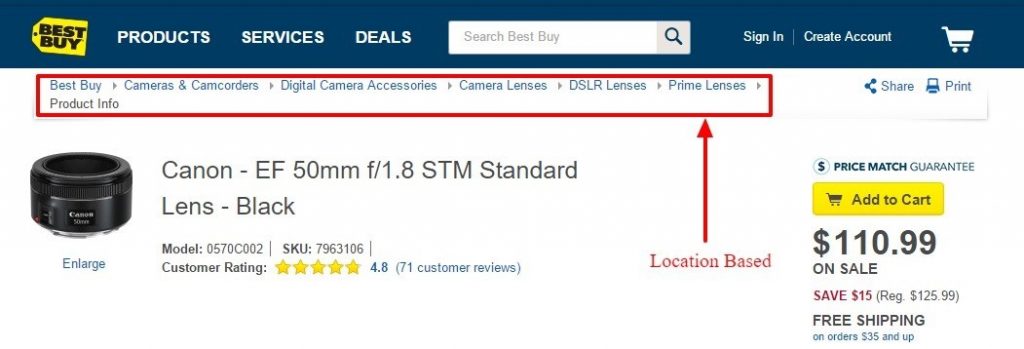
Image via VWO
A breadcrumb menu allows users to navigate to a previous page or category page or to the home page. It is a set of links located either at the top or bottom of a page. Breadcrumbs are highly recommended and useful to SEO, provided they have the proper schema.
A bread crumb menu serves two purposes:
To help users navigate a site without pressing the back button
To provide a hint to search engines about the structure of a website
SEO and Structured Data Markup
Structured data is gaining importance because Google uses it a lot in the Search Results.
Structured data is basically code that you add to your web pages, which is visible to search crawlers. It helps search engines understand your content’s context, in a language they understand.
Structured data, though about website content, has to do with technical SEO. This is because of the inclusion of code, which helps enhance your listings presentation on SERPs either through photo carousels, featured snippets, etc. and also increase your CTR (click-through rate).
Canonical URLs
All web pages should have a canonical URL. This URL is defined by adding the tag <link rel=”canonical” href=”yourpageurl”>, in the <head> of your pages and posts.
It’s a simple way to alert Google which page version to consider when indexing your website. It is similar in concept to your preferred domain, where a single page can be accessed through various URLs. Use rel=”canonical” when you have web pages with similar content, and also to avoid having duplicate content problems when you add content to your site from other websites.
Generally speaking, specify a canonical URL for all web pages.
Check your site to see if it provides a canonical URL by visiting any of your web pages, right-click at any point, and select VIEW SOURCE. Search for rel=canonical and also investigate the value.
If you cannot find a reference to canonical, use a plugin, and if you are on WordPress, use Yoast SEO or hire a developer. Once set up, you do not have to do anything else.
Optimize your 404 Page
A 404 page is shown when: a URL doesn’t exist, the page was deleted, or the URL was mistyped. WordPress themes have optimized 404 web pages by default – you can also edit your templates or use a plugin.
Don’t spend too much time on this. However, ensure that you have an optimized 404 page, in case a page is not accessible.
Optimize your XML Sitemap

Image via Reliable Soft
An XML sitemap is one of the most essential components of technical SEO. An XML Sitemap is a file that lists all posts/pages available on your website. Besides the title, it includes both published and updated dates.
Search engines use the XML sitemap as a guide when crawling a site.
XML sitemap optimization is straight forward. Simply include on your sitemap, web pages that are important for your site. More than not, these would be your posts, pages, and categories. Do not include in your sitemap, pages that do not have original content on their own, tag pages, or author pages. Ensure that your sitemap is updated each time you publish a new page on when a page is updated.
Submit your XML sitemap to both Google and Bing through Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools, and check the status.
Add SSL to Make your Site HTTPS
HTTPS is a ranking signal. Due to fraud cases involving credit cards, HTTPS establishes trust with users. Your website can only be accessed with HTTPS when you install SSL. This means that information transferred between the server and your site is encrypted, for example, passwords, personal data, etc.
Contact your hosting provider. Request that they enable SSL. Then follow a migration process that will activate SSL on your website without losing your rankings. Be careful not to miss any steps.
Website Speed – the Faster, the Better
Google rewards fast websites with higher ranks. So, the faster, the better.
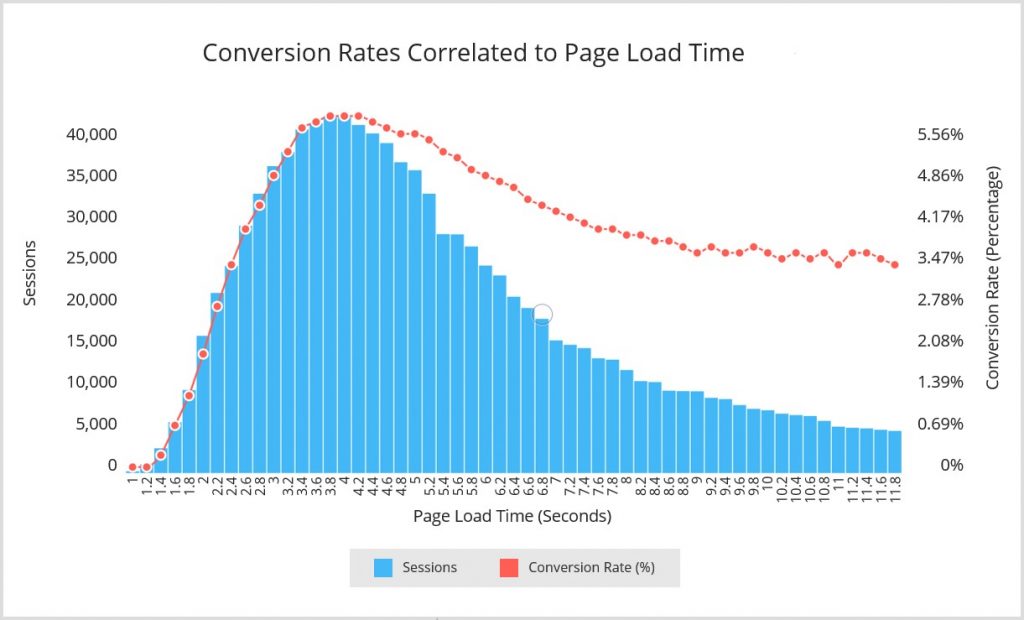
Image via Marketing Sherpa
Website speed speaks to your technical SEO needs, so if your site’s speed is slow, you will need to make changes to your site’s infrastructure.
First, check your speed by using three web tools: Pingdom tools, Google page speed insights, and Google mobile speed tool. They’ll provide recommendations on how to improve your websites speed.
Generally:
- Upgrade your server and use a 64 bits OS
- Upgrade to PHP 7.2> which will provide substantial speed improvements, compared to PHP 5.2
- Optimize image size without compromising HD quality
- Minimize plugin use
- Upgrade all WordPress plugins
- Don’t use heavy pre-made themes. Invest in a custom made theme
- Optimize and minify JS and CSS Files
- Use a caching plugin
- Avoid having too many scripts featuring in the <head> of your site
- Use asynchronous Javascript loading
Mobile Friendly
Your rankings will suffer if you do not have a mobile-friendly website – Google has a mobile-first index. Mobile-friendliness requires technical knowledge, but once it is properly configured, you will not need to deal with it again.
You should ensure that:
- Your mobile site should have the exact same content as your desktop
- Your site should load on your mobile device in less than six seconds
- Optimize your mobile website often, even though it is normal to experience lower conversion rates
- Avoid using popups on mobile
- Accelerated Mobile Pages do not replace your need for a fast-mobile website
Get Accelerated Mobile Pages
Google provided these to make mobile web faster. AMP HTML is a cut version of normal HTML. Once you create AMP pages, they are stored and given to users via a special Google cache, which is faster (loads almost instantly) than mobile-friendly pages.
AMP has both pros and cons.
AMP Pros:
- Makes pages on mobile sites load faster
- Increases CTR
AMP Cons:
- Difficult to implement
- AMP cannot be used for email marketing purposes
- Technical coding so that you’ll need to hire a developer
- Analytics and reports get confused due to the two different desktop and mobile website
